For Appointment, Contact.
+917099032777
Sun: Emergency Only
Mon - Sat : 10:00am to 4:00pm
Treatment and Prevention of Asthma: An In-Depth Guide
Dr. Kuntilraj Borgohain > Respiratory Medicine > Treatment and Prevention of Asthma: An In-Depth Guide
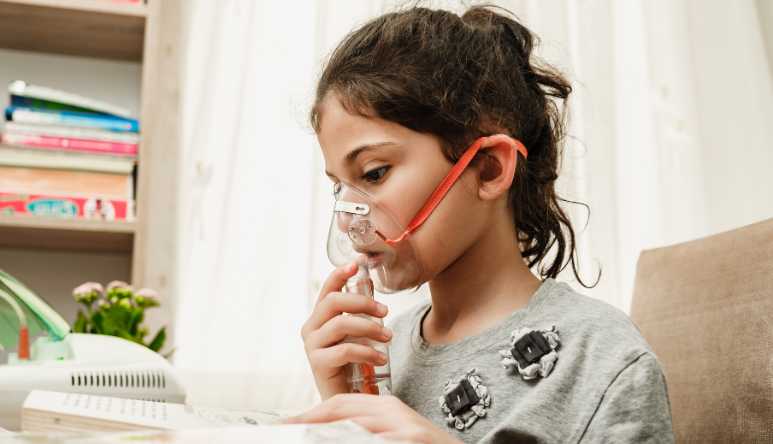
Asthma is a chronic condition that affects the airways leading to the lungs. During an asthma attack, the airways become inflamed and narrowed, making breathing difficult. According to the CDC, asthma affects over 25 million Americans. While there is no cure for asthma, it can be effectively managed through medications, avoidance of triggers, and lifestyle modifications. This guide provides an in-depth overview of the various treatment options available as well as preventive measures you can take to control your asthma.
Overview of Asthma
Asthma causes the inside walls of airways to become swollen and inflamed. This inflammation leads to increased mucus production and muscle spasms that constrict the airways. Common symptoms of asthma include:
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing
Asthma attacks or flare-ups can range from mild to life-threatening. Some factors that can trigger asthma attacks include:
- Allergens – dust mites, pet dander, pollen
- Irritants – cigarette smoke, air pollution
- Respiratory infections
- Physical activity
- Stress
- Cold air
- GERD
While asthma has no definitive cure, the right medications and lifestyle changes can help you successfully manage the condition.
Asthma Medications
Medications form the mainstay of asthma treatment. The most common types of drugs used are:
Inhaled Corticosteroids
Inhaled corticosteroids such as beclomethasone and budesonide help reduce airway inflammation. They need to be taken daily on a long-term basis to keep asthma under control.
Bronchodilators
Bronchodilators help relax the muscles around the airways to open them up and make breathing easier. They are further classified as:
- Short-acting bronchodilators – These provide quick relief from symptoms and are used as needed. Examples include albuterol and levalbuterol.
- Long-acting bronchodilators – These are taken daily to provide long-term control. Examples include salmeterol and formoterol.
Leukotriene Modifiers
Leukotrienes are chemicals that cause inflammation in the airways. Leukotriene modifiers such as montelukast block these inflammatory chemicals. They are taken daily.
Biologics
Biologics like omalizumab are monoclonal antibodies that target specific proteins in the immune system to reduce inflammation. They are used for patients with severe persistent allergic asthma.
Oral Corticosteroids
Oral corticosteroids like prednisone are used for short periods to treat severe asthma attacks. Prolonged use can cause side effects.
Your doctor will determine the right medications based on your level of asthma control, symptoms, and risk of flare-ups. Most people with persistent asthma need to be on daily long-term control medications along with a rescue inhaler for quick relief during attacks.
Avoiding Triggers
Avoiding potential triggers is key to keeping your asthma under control. Some steps you can take:
- Use allergen-proof covers for bedding and upholstered furniture.
- Use high efficiency filters in heating and cooling systems.
- Fix leaks, clean up mold, and maintain low indoor humidity.
- Keep pets out of bedrooms and bathe them regularly if pet allergies are a trigger.
- Avoid going outdoors when pollen and pollution levels are high. Wear a face mask if you do go out.
- Stay away from smokers and heavily polluted areas.
- Avoid scented candles and use unscented cleaning products.
- Take steps to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease if it triggers your asthma.
- Rinse your sinuses with saline solution and take medication during respiratory infections.
- Cover nose and mouth with a scarf in cold weather.
Keeping a diary to track your symptoms and their triggers can help you identify and subsequently avoid them.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Asthma Control
Making certain lifestyle changes can also help you manage your asthma more effectively:
- Maintain a healthy weight – Being overweight can worsen asthma symptoms. Losing weight may reduce inflammation.
- Quit smoking – Smoking is extremely harmful for people with asthma. Quitting can help prevent attacks.
- Exercise wisely – Walking, swimming, and yoga are less likely to trigger asthma than high intensity workouts. Use your inhaler before exercising.
- Manage stress – Find healthy ways to relax like meditation, listening to music, etc. Stress and anxiety can worsen asthma.
- Get your flu shot – Influenza can exacerbate asthma, so get the flu vaccine every year. Also get the pneumonia vaccine.
- Create an asthma action plan – Work with your doctor to create a written action plan for managing asthma day-to-day and handling attacks.
Making these lifestyle changes along with taking your medications can help you successfully control your asthma symptoms.
Preventing Asthma in Children
It’s important to take steps to lower your child’s chances of developing asthma if they are at risk, including:
- Breastfeed exclusively for at least 4-6 months. Breastfeeding strengthens the immune system.
- Ensure the mother does not smoke during pregnancy or after birth. Secondhand smoke increases asthma risk.
- Reduce exposure to indoor allergens and irritants by using allergen-proof covers, air filters, and unscented detergents.
- Do not allow smoking anywhere in the house or near children.
- Get recommended vaccinations like flu and pneumonia vaccines to prevent respiratory infections.
- Encourage children to maintain a healthy weight through proper nutrition and physical activity.
- Get children tested for allergies by an allergist and follow treatment guidance if allergies are identified.
Following these measures can help reduce the chances of your child developing asthma down the line.
Prevention Tips for Adults
Adults with asthma should take certain steps to prevent exacerbations and keep their asthma controlled:
- Take controller medications as prescribed even when asymptomatic to prevent attacks.
- Identify and avoid your specific asthma triggers.
- Get tested for allergies and follow treatment plans if you have allergies.
- Get a flu shot every year and follow your doctor’s advice on other vaccines.
- Monitor your lung function with regular spirometry tests.
- Carry your quick-relief inhaler with you at all times.
- Create and follow an individualized written asthma action plan with your doctor’s guidance.
Staying on top of your medications, avoiding triggers, and making lifestyle modifications can go a long way in helping you prevent asthma attacks and exacerbations as an adult.
The Takeaway
While asthma has no definitive cure, it is a highly manageable condition with the right treatment plan. The key is taking control medications regularly, avoiding triggers, making healthy lifestyle changes, and closely monitoring your symptoms. Work with an asthma specialist to come up with a tailored treatment regimen. With proper management, you can prevent asthma attacks and live an active, fulfilling life even with asthma.
.
Recent Comments
Recent Posts
-
 Treatment and Prevention of Asthma: An In-Depth Guide
30-Aug-2023
Treatment and Prevention of Asthma: An In-Depth Guide
30-Aug-2023
-
 Cystic Fibrosis: Symptoms and Treatment
16-Aug-2023
Cystic Fibrosis: Symptoms and Treatment
16-Aug-2023
-
 How Long Does It Take to Recover From Bronchitis?
13-Aug-2023
How Long Does It Take to Recover From Bronchitis?
13-Aug-2023




